Vehicle Evolution, Types, Technology, and the Future of Transportation
Vehicles have transformed the way people live, work, and connect with the world. From simple animal-driven carts to intelligent, self-driving machines, the evolution of vehicles reflects human innovation and changing societal needs. Today, vehicles are not just modes of transport but advanced systems combining mechanics, electronics, and digital technology.
Understanding Vehicles in Modern Society
A vehicle is any machine designed to transport people or goods efficiently. Vehicles support daily commuting, global trade, emergency services, and industrial growth, making them essential to modern infrastructure.
Importance of Vehicles
-
Enable personal mobility and independence
-
Support economic development and logistics
-
Improve access to education, healthcare, and markets
-
Save time and enhance productivity
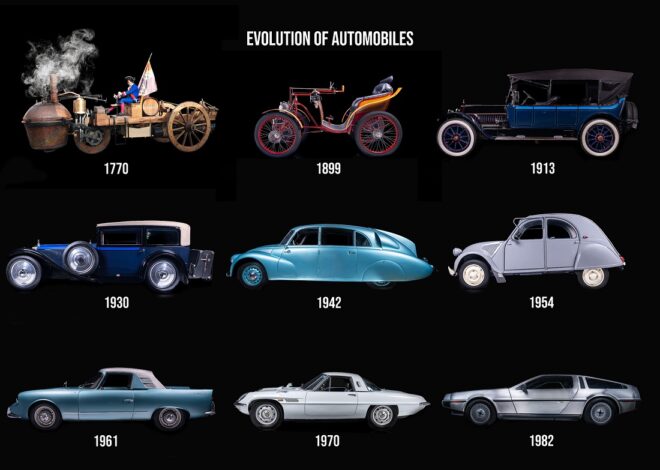
Evolution of Vehicles Over Time
The development of vehicles spans thousands of years and multiple technological revolutions.
Early Transportation Methods
-
Animal-powered carts and wagons
-
Canoes and sailing vessels for water travel
Mechanical and Industrial Advancements
-
Steam-powered engines and locomotives
-
Early gasoline-powered automobiles
Modern Vehicle Era
-
Mass-produced fuel vehicles
-
Introduction of electric and hybrid cars
-
Integration of software and digital controls
Types of Vehicles
Vehicles are categorized based on terrain, energy source, and purpose.
Based on Terrain
-
Land vehicles: Cars, buses, motorcycles, trucks
-
Water vehicles: Ships, boats, ferries
-
Air vehicles: Airplanes, helicopters, drones
Based on Energy Source
-
Petrol and diesel vehicles: Traditional internal combustion engines
-
Electric vehicles (EVs): Battery-powered and emission-free at use
-
Hybrid vehicles: Combination of fuel and electric power
-
Alternative fuel vehicles: Hydrogen, biofuels, and CNG
Based on Usage
-
Personal vehicles: Cars, scooters, bikes
-
Commercial vehicles: Delivery vans, trucks, buses
-
Special-purpose vehicles: Ambulances, fire engines, construction vehicles
Vehicle Technology and Key Components
Modern vehicles are complex systems designed for performance, comfort, and safety.
Essential Vehicle Components
-
Powertrain: Engine or electric motor
-
Transmission system: Transfers power to wheels
-
Chassis and body: Structural support and design
-
Suspension system: Ride comfort and stability
-
Braking system: Vehicle control and safety
-
Electronic systems: Infotainment, navigation, and sensors
Safety Innovations in Vehicles
Vehicle safety technology has significantly reduced road accidents and fatalities.
Common Safety Features
-
Airbags and seatbelts
-
Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)
-
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
-
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS):
-
Lane departure warning
-
Adaptive cruise control
-
Automatic emergency braking
-
Environmental Impact of Vehicles
Traditional fuel vehicles contribute to air pollution and climate change. This has led to a global push for cleaner transportation alternatives.
Sustainable Vehicle Solutions
-
Growing adoption of electric vehicles
-
Development of hydrogen-powered vehicles
-
Improved fuel efficiency standards
-
Use of lightweight and recyclable materials
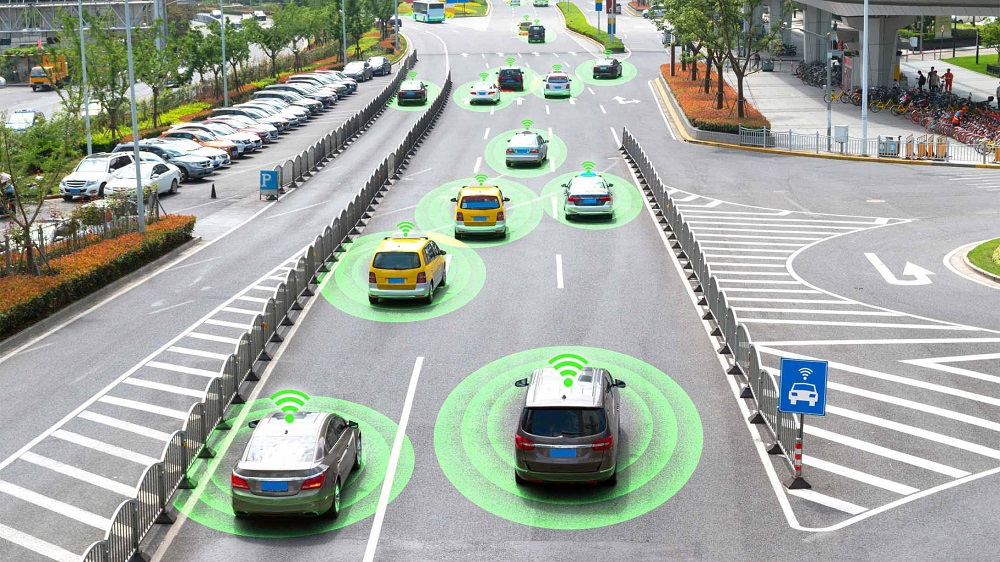
The Future of Transportation
The future of vehicles is driven by innovation, sustainability, and connectivity.
Emerging Trends
-
Autonomous vehicles: Reduced reliance on human drivers
-
Connected vehicles: Real-time communication with infrastructure
-
Shared mobility: Ride-sharing and subscription-based ownership
-
Smart cities integration: Vehicles working with intelligent traffic systems
Benefits and Challenges of Modern Vehicles
Benefits
-
Faster and more comfortable travel
-
Enhanced safety and reliability
-
Economic growth and employment opportunities
Challenges
-
Traffic congestion in urban areas
-
Environmental concerns from emissions
-
Charging and fueling infrastructure gaps
-
Data privacy and cybersecurity risks
Conclusion
Vehicles continue to shape the future of transportation by combining advanced technology with sustainable practices. As innovation progresses, the focus is shifting toward cleaner, smarter, and safer vehicles, ensuring efficient mobility while minimizing environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the main purpose of a vehicle?
The primary purpose of a vehicle is to transport people or goods safely and efficiently.
2. How are electric vehicles different from fuel vehicles?
Electric vehicles use batteries instead of fuel engines, producing lower emissions and requiring less maintenance.
3. What technologies make vehicles safer today?
Technologies like airbags, ABS, ESC, and ADAS significantly improve vehicle safety.
4. Are autonomous vehicles completely driverless?
Most current autonomous vehicles still require human supervision, though full automation is under development.
5. How do vehicles contribute to environmental pollution?
Fuel-powered vehicles emit greenhouse gases and pollutants that affect air quality and climate.
6. What factors should be considered when choosing a vehicle?
Key factors include budget, fuel efficiency, safety features, maintenance costs, and intended use.
7. Will electric vehicles replace all fuel vehicles in the future?
While EV adoption is increasing, a complete replacement will depend on infrastructure, cost, and technological advancements.
Related Posts
How Vehicles Evolved and Shaped Modern Transportation

Tips for Buying a Used Car


